ELD Mandate in Canada

Expedited enforcement of ELD in Canada
Currently, the Canadian Council of Motor Transport Administrators (CCMTA) is finalizing the technical standards of ELDs. There is a good chance that the rule will be published by the end of 2019 for its mandate starting from 2020 with an extended compliance date in 2022. The ELD mandate in Canada is supposedly to be mirrored with the ELD mandate in the U.S. with ELD already mandated in the U.S., majority of fleet companies in Canada have started preparing for the ELD mandate and using them in advance to allow a smooth transition from paper logs to electronic logging devices.
Benefits for Fleet and drivers
More Safety– It is one of the main purposes of using ELD’s. Drivers are constantly reminded about their rest breaks. Hence, fatigue is reduced, and drivers are less prone to accidents. Thus, increases fleet’s overall safety.
Replacement of paper logs– Using Electronic logging devices allows drivers to be hassle free as ELD’s record automatic readings and data can be stored electronically. This saves driver’s time and money.
Compliance with regulations- By using ELD’s drivers remain in constant compliance with the U.S and Canada regulations. The ELD’s make sure the drivers stay in compliance by giving them a foretime warnings and indications of their violations.
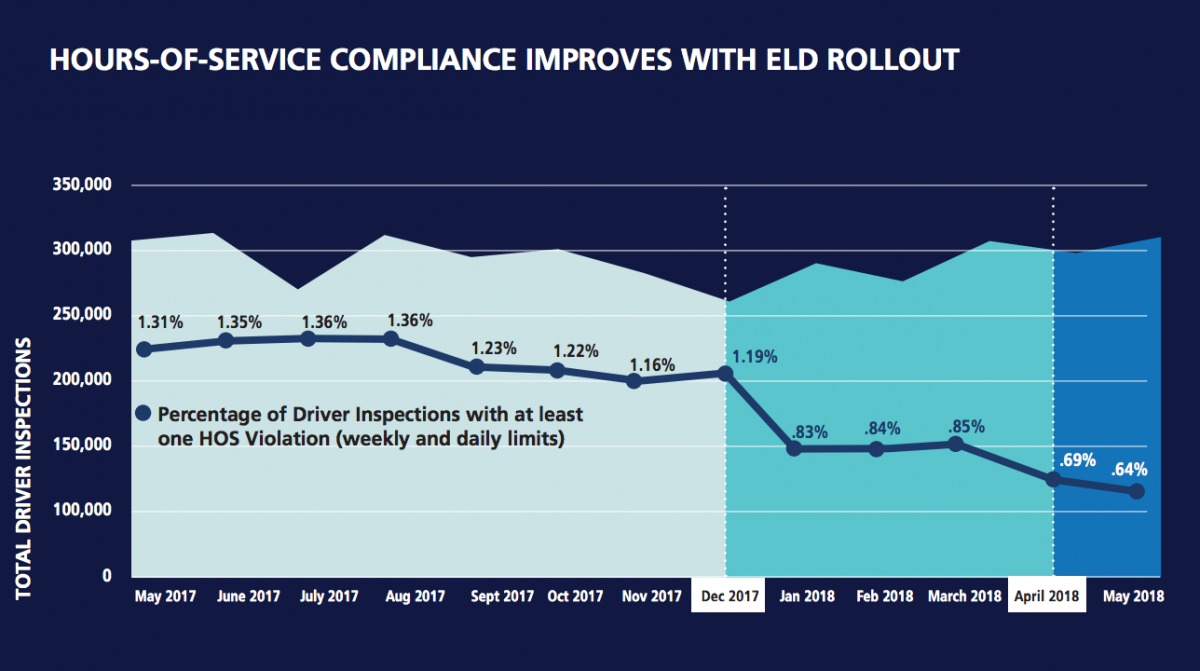
Reduction of Errors and Tampering of driver’s hours of service (HOS)- ELD usage has reduced the violations and editing of annotations. Only limited entries are editable, the mistakes by the drivers can be corrected by both the authorized carrier staff and driver with an annotation (note) explaining the reason for their editing. Also, the drivers are not permitted to tamper with the drive time and hours available for driving.
Our ELD, is fully compliant with both Canadian and U.S regulations with additional features such as driver behaviour. Easy to use, automatic switching to US or Canadian regulation when crossing the border, automatic switching from driving to on-duty during traffic. We offer wide range of integrated solutions for transportation industries such as Dispatch Software, Border Crossing, GPS Tracking.
Disclaimer- The rules and regulations are subject to change any time. Readers must verify with the authority, FMCSA / MTO and must not rely on the contents of this blog.